 Mazhuang Village, Yuhe Town, Huixian City, Xinxiang City, Henan Province, China
Mazhuang Village, Yuhe Town, Huixian City, Xinxiang City, Henan Province, China
 Service Hotline +86 17630258963
Service Hotline +86 17630258963  Cell phone +86 17630258963
Cell phone +86 17630258963 Thrust ball bearing: simple structure, low friction coefficient. Suitable for medium load and high speed rotation. Commonly used in small motors, automobile transmissions, etc.
Thrust roller bearing: higher load capacity than ball bearing, suitable for heavy load. Suitable for medium to low speed operation. Commonly used in heavy machinery, industrial equipment, etc.
Thrust needle bearing: needle-shaped rolling element, suitable for applications with limited space but high load. Used in light industrial machinery, precision equipment, etc.
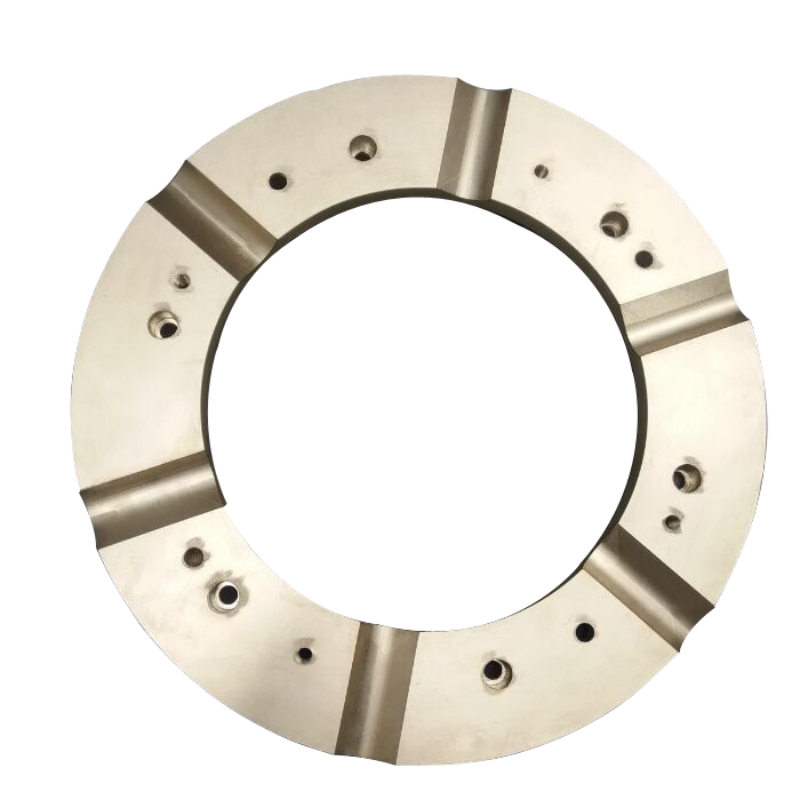

One-way thrust bearing: can only withstand axial force in one direction. Commonly used in equipment where axial force comes from only one direction.
Bidirectional thrust bearing: can withstand axial force in both directions. Commonly used in equipment that needs to withstand reverse axial load.
Rolling thrust bearing: withstands axial force through rolling elements (balls, rollers, needles). Has a lower friction coefficient and higher efficiency.
Sliding thrust bearing: withstands axial force through sliding surfaces (usually metal to metal or metal to composite materials). Suitable for occasions that need to withstand larger loads and lower speeds.
