 Mazhuang Village, Yuhe Town, Huixian City, Xinxiang City, Henan Province, China
Mazhuang Village, Yuhe Town, Huixian City, Xinxiang City, Henan Province, China
 Service Hotline +86 17630258963
Service Hotline +86 17630258963  Cell phone +86 17630258963
Cell phone +86 17630258963 Copper bushing spectrometer usually refers to a spectral analysis instrument used to detect the composition of copper bushings (copper alloy components). This equipment detects the chemical composition and content of copper bushing materials by analyzing the spectra of the material to ensure that the material meets the required alloy composition standards. The following is a detailed explanation of the copper bushing spectrometer:
Spectrometers are based on the principle of spectral analysis, which utilizes the spectra emitted or absorbed by a sample under the action of electromagnetic radiation to identify and quantify the elements in it. Common types of copper jacket spectrometers include:
Emission spectrometers (e.g. Spark Emission Spectrometer, OES): the surface of a copper jacket sample is excited by a spark or arc, causing it to emit characteristic spectra, which are analyzed by the spectrometer to identify the chemical composition in the sample.
X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF): using X-rays to irradiate the copper bushing, resulting in the production of secondary X-rays, and analyzing the characteristics of these X-rays to detect the alloy composition.
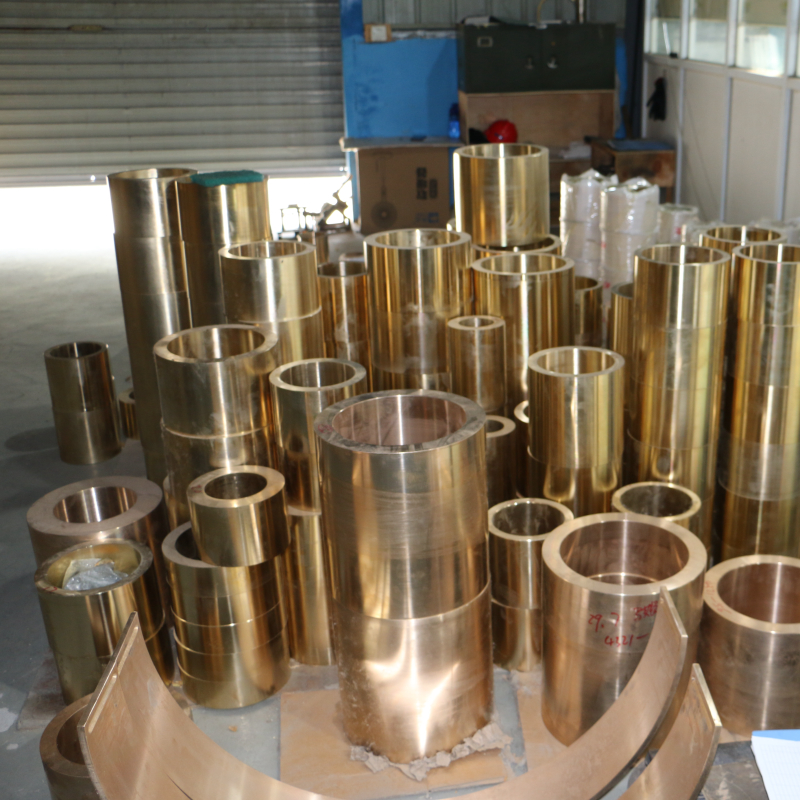

Composition testing: To ensure that the content of copper and alloying elements (e.g. tin, lead, zinc, aluminum, etc.) in copper bushings meets standards. For example, bronze, brass and other materials often used in copper bushings, the proportion of each element directly affects its performance.
Quality control: In the production of copper bushings, spectrometers can be used for quality testing during the production process to ensure that the material composition meets design and standard requirements.
Alloy identification: The spectrometer can quickly identify the type and composition of copper alloys and is suitable for the classification and inspection of different copper alloy materials.
