 Mazhuang Village, Yuhe Town, Huixian City, Xinxiang City, Henan Province, China
Mazhuang Village, Yuhe Town, Huixian City, Xinxiang City, Henan Province, China
 Service Hotline +86 17630258963
Service Hotline +86 17630258963  Cell phone +86 17630258963
Cell phone +86 17630258963 Appearance:
The gap between the copper bushing and the flange is clearly visible, with the naked eye or a simple measuring tool to detect a large gap. For example, when inserted between the copper sleeve and the flange with a plug ruler, the thickness of the plug ruler is larger, indicating that the gap is beyond the normal range.
Impact on equipment:
Inaccurate positioning: Due to the large gap, the position of the copper bushing in the flange cannot be accurately fixed, and may wobble and shift during the operation of the equipment. This will affect the working accuracy of other parts associated with the copper sleeve, such as the rotation accuracy of the shaft is reduced, resulting in unstable output of the equipment.
Increase in vibration and noise: Excessive clearance will make the contact between the copper bushing and the flange not tight, which will easily generate vibration when the equipment is running. This vibration will be transmitted to the whole equipment, which will not only cause noise pollution, but also may cause damage to the structure of the equipment and accelerate the wear and fatigue damage of the parts.
Risk of leakage: If the fit of the copper sleeve to the flange is used to seal fluids or gases, an excessive gap can lead to an increased risk of leakage. For example, in pipeline connections, leakage of media may occur, affecting the normal operation of the system and even causing safety hazards.
Reduced load carrying capacity: When the fit tolerance is too large, the contact area between the copper bushing and the flange is reduced and the load cannot be transferred effectively. This will lead to a larger load, the copper sleeve is prone to deformation or damage, reducing the load-bearing capacity of the equipment.
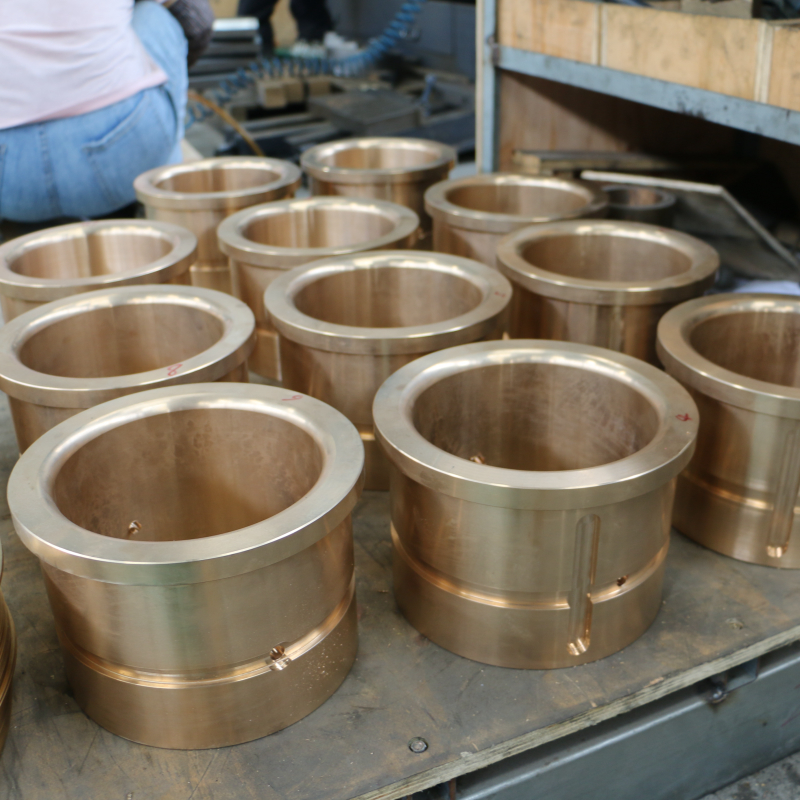

Appearance:
copper bushing and flange installation difficulties, may need to use external force forced assembly. After installation, there is almost no gap between the copper sleeve and the flange, and the copper bushing may even be “bitten” by the flange.
Impact on equipment:
Excessive assembly stress: Too small a fit tolerance can lead to large assembly stresses during assembly. These stresses may cause deformation of the copper bushing or flange, or even damage such as cracks. For example, when an interference fit is used, if the amount of interference is too large, it may cause the copper bushing to be crushed during the installation process.
Thermal Expansion and Contraction Problem: When the temperature of the equipment changes during operation, there is not enough space to accommodate the thermal expansion and contraction of the material due to the tight fit between the copper bushing and the flange. This can cause parts to be overstressed when the temperature rises, or loose when the temperature drops.
Increased Friction and Wear: An overly tight fit can increase the friction between the copper bushing and the flange, which tends to generate excessive heat when the equipment is in operation, leading to an increase in the temperature of the part. This will not only reduce the efficiency of the equipment, but also accelerate the wear and tear of the copper sleeve and flange, shortening their service life.
Difficulty in maintenance: Once the copper bushing and flange are too tightly fitted, disassembly becomes very difficult when the parts need to be repaired or replaced. It may be necessary to use destructive methods to remove the copper bushing from the flange, increasing the cost and time of maintenance.
