 Mazhuang Village, Yuhe Town, Huixian City, Xinxiang City, Henan Province, China
Mazhuang Village, Yuhe Town, Huixian City, Xinxiang City, Henan Province, China
 Service Hotline +86 17630258963
Service Hotline +86 17630258963  Cell phone +86 17630258963
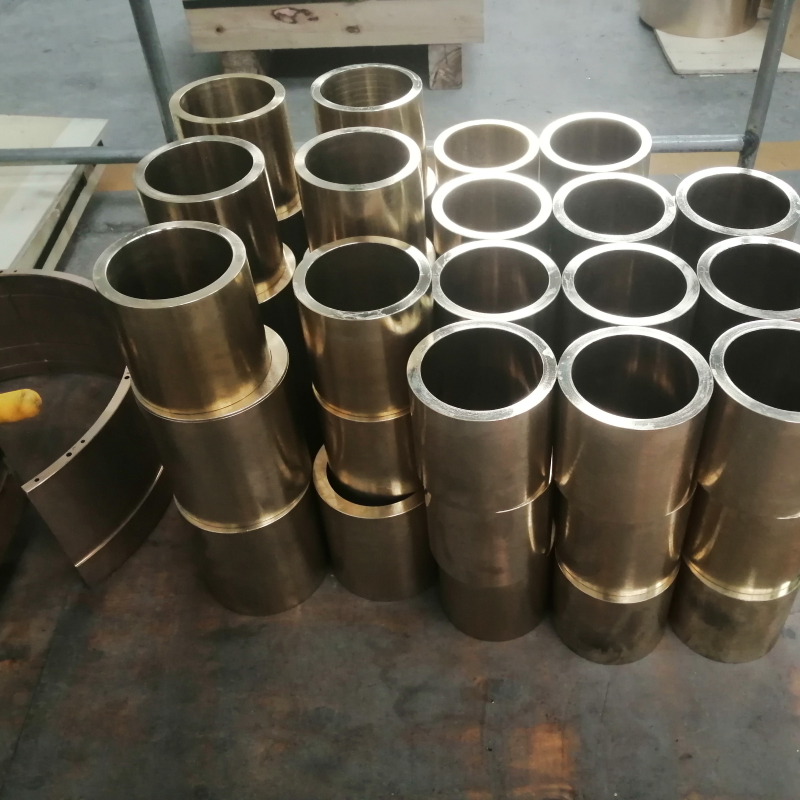
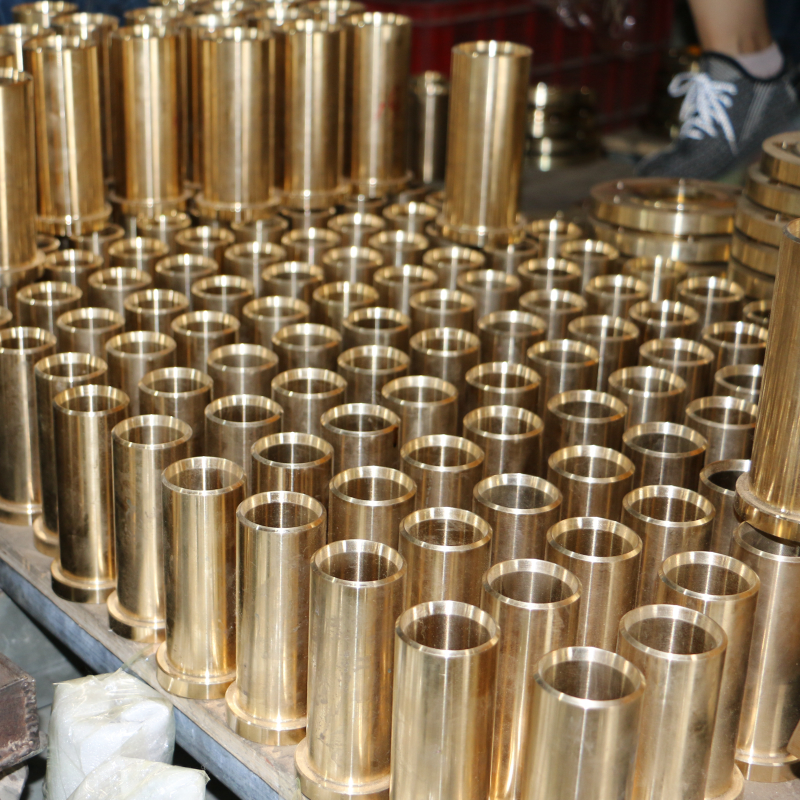
Cell phone +86 17630258963 Copper sleeves are prone to defects during the casting process, such as porosity, inclusions, cold segregation, shrinkage, cracks, and so on. In order to avoid these defects, the following are some common preventive measures:
Correct choice of casting method: according to the size, shape and use requirements of the copper sleeve to choose the appropriate casting process, such as sand casting, centrifugal casting, metal casting and so on. For copper sleeves that require high precision and high strength, centrifugal casting and metal casting are more effective.
Control pouring speed: too fast or too slow pouring speed will lead to defects in the copper sleeve. Too fast may cause turbulence and bring in gases and impurities, while too slow is prone to cold segregation or incomplete filling. The appropriate pouring speed should be determined according to the fluidity of the copper liquid and the characteristics of the casting model.
Appropriate melting temperature: too high a melting temperature will lead to an increase in the solubility of gases in the copper liquid, the formation of porosity, too low may lead to poor fluidity of the copper liquid, prone to cold segregation or shrinkage holes. Usually control the pouring temperature of copper liquid in the appropriate range to avoid overheating or overcooling, to reduce the appearance of defects in copper sleeves.
Prevent oxidation: copper liquid is easily oxidised during melting and pouring, resulting in the formation of oxidation inclusions. A covering agent should be used to protect the melt during melting to reduce the contact between the copper liquid and air and prevent oxidation.

Degassing treatment: gases such as hydrogen are easily dissolved in the copper liquid, leading to porosity defects. The use of degassing agent or the use of argon stirring and other methods to remove the gas in the copper liquid can effectively reduce the generation of copper sleeve porosity.
Reasonable design of casting and pouring system: Ensure that the casting and pouring system design is reasonable, so that the copper liquid can fill the cavity smoothly, and ensure the proper solidification sequence. Good pouring system design can avoid turbulence, gas entrainment and segregation problems.
Uniform cooling: Avoiding too fast or too slow localised cooling of the copper sleeve can be achieved by controlling the casting temperature or by setting up an appropriate cooling system. Too fast cooling is prone to thermal stress and cracks, while too slow cooling is prone to shrinkage.
Strictly control the alloy composition: The improper proportion of the composition of bronze or brass can easily cause casting defects. Impurity elements (such as lead, phosphorus, zinc, etc.) in the alloy, if the content is too high, will reduce the material properties and increase the risk of casting defects. High purity raw materials should be used and the content of each element should be strictly controlled.
Preheat casting: In metal mould casting or sand casting, preheating the casting helps to improve the fluidity of the copper liquid and reduce the generation of defects such as cold segregation and cracks. In particular, metal mould preheating can prevent cracks caused by thermal stress.

Heat treatment: some copper sleeve castings in the casting is completed, you can improve its internal structure through appropriate heat treatment to eliminate internal stress, to prevent the further development of cracks.
Surface treatment: the surface of the casting copper sleeve cleaning, such as grinding, polishing, etc., to remove the surface of the oxide layer and small defects, to ensure the surface quality of the casting.
Process monitoring: Each process parameter (such as temperature, pouring speed, cooling speed, etc.) should be strictly monitored during the casting process, and the copper sleeve should be inspected on-line through non-destructive testing (such as ultrasonic testing, ray testing), so as to detect problems in time.
Quality control: through chemical analysis, metallographic analysis and other methods of alloy composition and grain organisation to ensure that the casting materials and processes meet the requirements.
Through these measures, can significantly reduce the casting process of copper sleeve defects, improve the quality and service life of copper sleeve.
