 No. 16, 2nd Floor, Unit 2, Building 1, Geohome, at the intersection of Yushinan Road, Science Avenue, Zhengzhou High-tech Industrial Development Zone
No. 16, 2nd Floor, Unit 2, Building 1, Geohome, at the intersection of Yushinan Road, Science Avenue, Zhengzhou High-tech Industrial Development Zone
 Service Hotline +86 17719955658
Service Hotline +86 17719955658  Cell phone +86 17719955658
Cell phone +86 17719955658 Annealing
Stress relief annealing: Tin bronze can be stress relief annealed. During casting, cold working, etc., tin bronze generates internal stresses. Stress relief annealing can eliminate these internal stresses, generally at a temperature of about 200 - 300 ℃. For example, for tin bronze parts that have been deformed by cold working, stress relief annealing reduces the likelihood of deformation or cracking during subsequent use of the part.
Recrystallization annealing: Tin bronze is also capable of recrystallization annealing. When the tin bronze after a large degree of cold deformation, through the recrystallization annealing can make the deformation grain recrystallization for the equiaxed grain, thus improving the material properties. Recrystallization annealing temperature is usually between 600 - 700 ℃, appropriate recrystallization annealing can improve the plasticity of tin bronze, reduce its hardness, and is conducive to subsequent processing, such as further cold stamping or drawing.
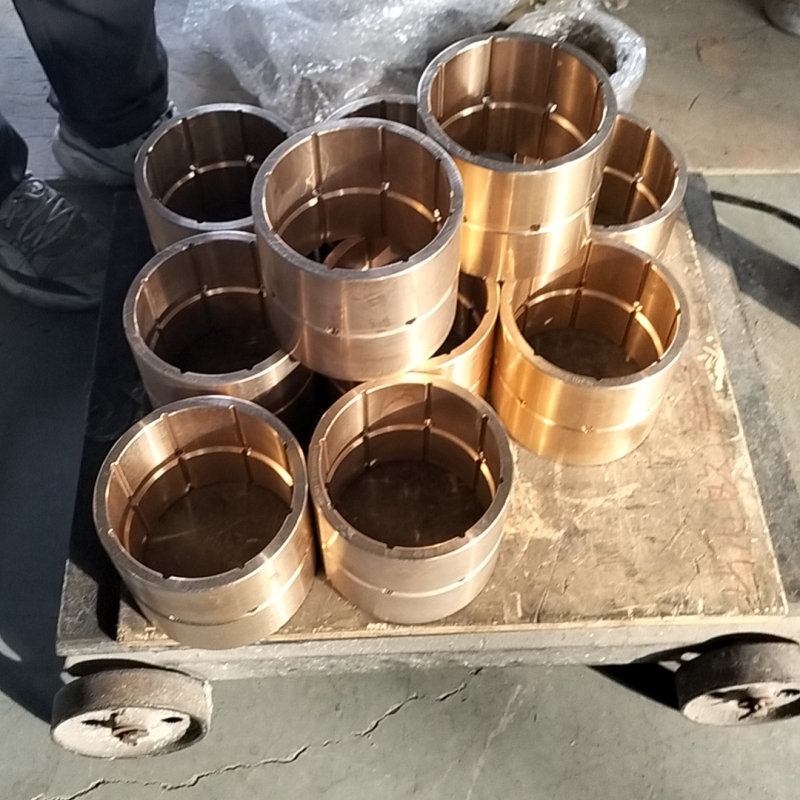

Quenching and aging treatment
The effect of quenching and aging treatment of tin bronze is not as pronounced as that of materials such as aluminum alloys. However, some tin bronzes with special compositions (e.g., containing small amounts of aluminum, titanium, etc.) can be strengthened by quenching and aging treatments. The quenching and aging temperatures and times need to be determined according to the specific alloy composition. Quenching generally involves heating the alloy to a high temperature and then cooling it rapidly, while aging involves holding it at a lower temperature for a longer period of time to increase the strength and hardness of the alloy through the precipitation of reinforcing phases. However, the application of this strengthening method in tin bronze is relatively small, mainly relying on the alloy composition and work hardening and other ways to improve performance.
